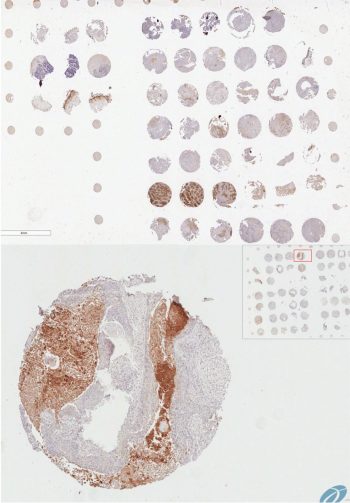
The Serine protease inhibitor superfamily consists of 16 clades of evolutionarily and structurally conserved proteins, many of which have protease inhibitory activity. Several of the SERPINs have been implicated in the development and spread of cancer, and we have shown that SERPINB3, a cysteine protease inhibitor that targets lysosomal cathepsins, is important for resistance to radiation. A main focus of the lab is to understand the critical roles of these proteins, namely the intracellular SERPINB3, in cancer pathogenesis and resistance to therapy.